I doubt that members of the Salonika Campaign Society really need International Women’s Day to remember the service and sacrifice of the women of the Scottish Women’s Hospital who served in the Balkans. The Society has remembered them in books, in talks and presentations, at events and in articles, both printed and online. Even so, it may be helpful to have a reminder of these redoubtable women and their noble enterprise, through the graves of just four of their number. I photographed these on a visit to Thessaloniki ten years ago, at the CWGC Lembet Road Military Cemetery. They are: Sister Mary de Burgh Burt, Sister Florence Missouri Caton, Masseuse Olive Smith and Alice Annie Grey.
Continue reading “Remembering …”Tag: Medical Services
The medical services and their activities in the Macedonian Campaign of 1915-1918.
The Sinking of the Rewa
Last year I resolved to share the story of the sinking of the hospital ship, Rewa. I decided to do this on the anniversary of the event in 2026. The trouble was, I failed to check the date and, convinced that it was in February, by the time I looked up the details I realised I had missed it – 4 January! I could have left it until 2027 but, instead, decided to post the story today, Fred Braysher’s birthday, as it was Fred (my grandfather) who told me the story 44 years ago.
Continue reading “The Sinking of the Rewa”Nick Ilić lecture on the ‘Serbian Golgotha’
Apologies for the late notice…
Tonight (Monday 9th February) at 7pm, Nick Ilić will be giving a free online talk (as part of the Serbian Council of Great Britain Serbian Month programme of events).
Nick says on ‘X’, “The talk is about the ‘Second Serbian Campaign’ that was taking place 110 years ago during the Great War. The events culminated in what became called the ‘Serbian Golgotha’ – where rather than surrender to the advancing German, Austro-Hungarian and Bulgarian Armies, the Serbs decided to retreat over the Albanian and Montenegrin mountains to the Adriatic Coast. Thousands perished.
The Serbs did not march on their own over the mountains – with them went the international military and medical missions that had deployed to Serbia in 1914 and 1915.
It is a most remarkable, heroic, tragic and little known story.
The events also witnessed the deployment of the French and British Salonika Armies to come to the rescue of the Serbs – but to no avail.”
To access the talk:
Join Zoom Meeting
https://us06web.zoom.us/j/88643782272?pwd=NMRfjni3cQdTiGy3bLvMDeNAgzYxeb.1
Meeting ID: 886 4378 2272
Passcode: 443996 from this page.
Mettle and Steel: the AANS in Salonika
Searching for information recently about nursing in Salonika, I stumbled across Mettle and Steel: the AANS in Salonika. It’s an account of the punishing nature of Australian military nursing in Salonika. From 1917, Australian nurses were sent into this difficult and unfamiliar theatre of war to relieve the British, French and Canadian nurses and to provide nursing care to British soldiers and prisoners of war. As nursing ‘our boys’ was a major motivation for overseas service, it was something of a disappointment for many that they could not nurse Australian soldiers.
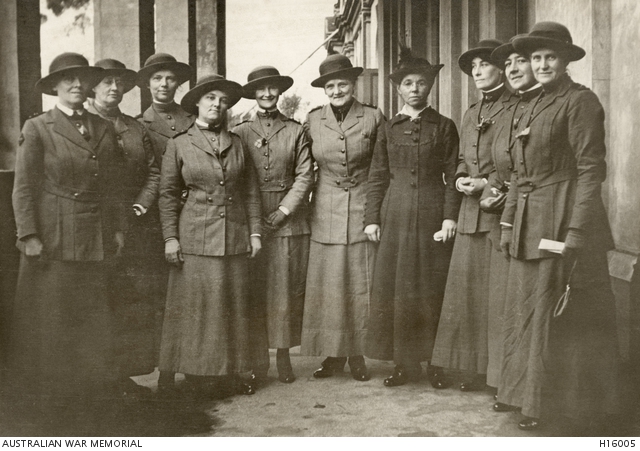

A group of Australian Army nurses about to depart from Adelaide for Salonica, 14 June 1917. From the left: Miss Molly Wilson, Mrs J. Tyers, Miss Edith Horton, Miss Marion Geddes, Miss Laura Begley, Mrs Jessie McHardie White (Principal Matron), Mrs Forsyth (wife of General Forsyth), Miss Violet Mills (Matron of No 5 Australian General Hospital who was on a visit to Adelaide), Miss Alice Prichard and Miss Florence G. Gregson.
I hadn’t quite appreciated the scale and complexity of the Australian nursing presence: four contingents were dispatched via Egypt, under constant U-boat threat, and then distributed across a shifting network of British hospitals in Greece and the surrounding hills. Each unit was allocated one Matron, ten AANS Sisters and eighty Staff Nurses. The nurses were led by senior matrons such as Jessie McHardie White, who oversaw not only clinical standards but the welfare and morale of hundreds of nurses. Staff Nurse Lucy May’s personal account helps convey the experience of Salonika in winter:
[12 October 1917] Water racing thru wards & reached halfway up bedsteads, haversacks, boots, socks, pants floating down road…
[21 October] Lanterns blowing out & leaving you in dark…
[23 October] Still don weather attire, only wearing men’s pyjama pants, putties, gum boots, man’s shirt also. Had dress tucked around waist all night…
[2 November] Imagine me [on night duty] over my ankles in mud, dragging one foot out then other foot & standing on one leg in grim peril or sitting down hastily…feeling the rain oozing through my mack. This is the life?”
As winter ended, the nurses then faced oppressive summers dominated by malaria. The AANS uniform was adapted in an attempt to counter the mosquito risk. A ‘mosquito proof’ nurse would be clad in her working dress, huge gloves, rubber boots and thick veil which, according to Lucy Tydvil Armstrong:
“made it quite impossible to carry out our duties, when men were rigoring and vomiting all night long, we just had to do away with the precautions, & run the risk of being bitten with mosquitos.”

A group of Australian Army Nursing Service nurses at the 52nd British General Hospital at Kalamaria, Greece ready for night duty wearing headdress provided for protection against mosquitoes. C 1918.
Despite the precautions, Matron McHardie White later reported that, ‘most of the nurses were affected by it [malaria] one time or another…’ By August 1918 45 nurses had been sent back to Australia from Salonika and another 14 were waiting to go, mostly on grounds of ill health. The death of Sister Gertrude Evelyn Munro in 1918 underlines the very real cost of the AANS service.

Sisters Gertrude Evelyn Munro and Amy Christie of the AANS. The photograph was probably taken at the 60th British General Hospital, Salonica.
Despite deteriorating health and official doubts about the value of their continued presence, the nurses remained in Salonika until after the war ended, not returning home until early in 1919. Their courage and professionalism were acknowledged through praise and decorations from British, Serbian and Greek authorities. Matron McHardie White, as just one example, was awarded the Serbian decoration of the Order of St Sava and was made a Member of the British Empire.
Nurses’ Narratives
It’s always interesting to read first-hand accounts of experience and so it was good to see that some diary and retrospective narratives written by the AANS nurses have been, and are being, transcribed. Staff Nurse Vivian A Lee Shea, for example, recalled,
We arrived in the midst of summer & the height of the Malaria & Dysentry season, & work commenced right away. We had much to learn. We were all new to each others ways & the medical Staff & personnel had only just landed as we ourselves had.
The Hospital was rather well situated at an elevation of about 2000 ft above sea level & this gave us a cooler summer, but made it impossible to live there in the winter months. During the winter months we occupied the Prisoners of War Hospital in the Base area. Here we nursed British Troops, as well as prisoners of War, the latter were representatives from practically every one of the Baltic States. Germans Bulgars, Turks, Romanians, Greeks Albanians & Serbs, in fact any one found in enemy lines.
Annie E Major-West remembered,
We remained in Salonika till February 1919, during the whole time the work was very heavy at times the hours on duty were particularly long. these conditions were occasioned by the prevalence of Sickness amongst the Sisters and Medical Officers.
Frequently the Bulgars & Germans were over in Planes endeavouring to bomb
the Town but the Vicinity of the Hospital was never damaged, during the Month
of August 1917 the town was partially destroyed by fire, Supposed to have
been the work of Spies.
- Read the full article Mettle and Steel: the AANS in Salonika.
- Search for first hand accounts here: https://transcribe.awm.gov.au/transcription
“A Girl Should Have Her Opportunity”: Two Heroines in Fiction in Salonika
The Salonika Campaign Bibliography, researched and compiled by SCS Member Keith Roberts, is a fantastic resource for those researching or delving deeper into the campaign. Now in its sixth edition, it lists over 480 entries from a variety of sources. Interestingly, these sources also include novels and literature. Although literature isn’t usually a source for historically accurate facts, it has a role in helping to understand, to some degree, the experience and attitudes of others in other times.
With that in mind, and having recently been reading about the service of nurses in the campaign, two novelists from Keith’s list piqued my interest: Bessie Marchant and May Wynne the authors, respectively, of A V.A.D. in Salonika and An English Girl in Serbia – both novels written primarily for a young audience.
A V.A.D. in Salonika (1917) follows a young British woman, Joan Haysome, who volunteers to serve as a V.A.D. (Voluntary Aid Detachment) nurse in Salonika. The plot is full of unlikely coincidences as Joan, determined to prove her worth, and atone for a past mistake, attempts to stop a German spy within the Allied ranks. It is a novel of its time, and for that reason, interesting in the way it reflects diffierent contemporary attitudes towards women volunteering in the war effort.
The inspector bowed, looking properly impressed, but he had his private opinion all the same as to the use of young ladies in V.A.D. work. To his way of thinking, if one of the leisured classes set about trying to do something useful, it meant that a servant of some sort was necessary to do the work over again. Rich folks had their place in the scheme of creation, but their place was mainly to provide honest employment for other people.
Joan is not a passive or submissive figure. Marchant frequently describes Joan’s thought processes as she struggles to overcome doubts and crises of confidence to show courage, resourcefulness, and responsibility for others.

In An English Girl in Serbia (1916), two 16-year-old twins, Nancy and Tom Allerson, become caught up the turmoil of wartime Serbia. This is more of a “ripping yarn” involving danger and dramatic adventure. There is a little more detail about the war than in Marchant’s novel, with a depiction of the Serbian retreat from the Bulgars. Nancy has far less introspective reflection than Joan but the story does paint Nancy as an active, resourceful survivor determined to see the ordeal through.

Both novels follow a tradition of daring adventure stories for boys but in these the focus shifts to central female characters and, particularly in A V.A.D. in Salonika, contemporary attitudes to women in war,
“But don’t you think that the girls want to do their bit as well as the boys? The harder the work the greater the patriotism. A girl should have her opportunity, and she may be trusted to rise to it.”
I quite enjoyed reading the two books, which are fast-paced and easy to read. In these ‘enlightened’ times, An English Girl in Serbia would probably come with a trigger warning regarding some of its language and attitudes! It is, perhaps, more interesting from a historical point of view with its references to the Serbian retreat and comitadji. And, although the plot in A V.A.D. in Salonika relies too heavily on coincidence, the novel is more thoughtful. Joan is a much more interesting and developed character and, as such, the book may be seen as part of the wider body of literature that helped shape British public opinion about the role of women in war.
My thanks go to Keith for adding these titles to the SCS Bibliography:)
More…
The Sinking of the Marquette, 1915
A little over 110 years ago, on Saturday 23 October 1915, the British transport ship Marquette was torpedoed by the German submarine U-35 as it entered the Gulf of Salonika. The ship sank within ten minutes. Of the 741 people on board, 167 died, including 32 New Zealanders – ten of whom were nurses.

The New Zealand Nurses
Most of the New Zealanders aboard were members of the 1st New Zealand Stationary Hospital. They had been serving in Egypt, treating casualties from Gallipoli, and were being transferred to support Allied operations in the Balkans. Among them was Staff Nurse Margaret Rogers, who had enlisted only months earlier in July. Indeed, The New Zealand Army Nursing Service was itself new and only established early in 1915.

Image source: Nurse Margaret Rogers, URL: https://nzhistory.govt.nz/media/photo/nurse-margaret-rogers, (Manatū Taonga — Ministry for Culture and Heritage), updated 28-May-2024
The Marquette, originally a cargo vessel, had been adapted for wartime transport.
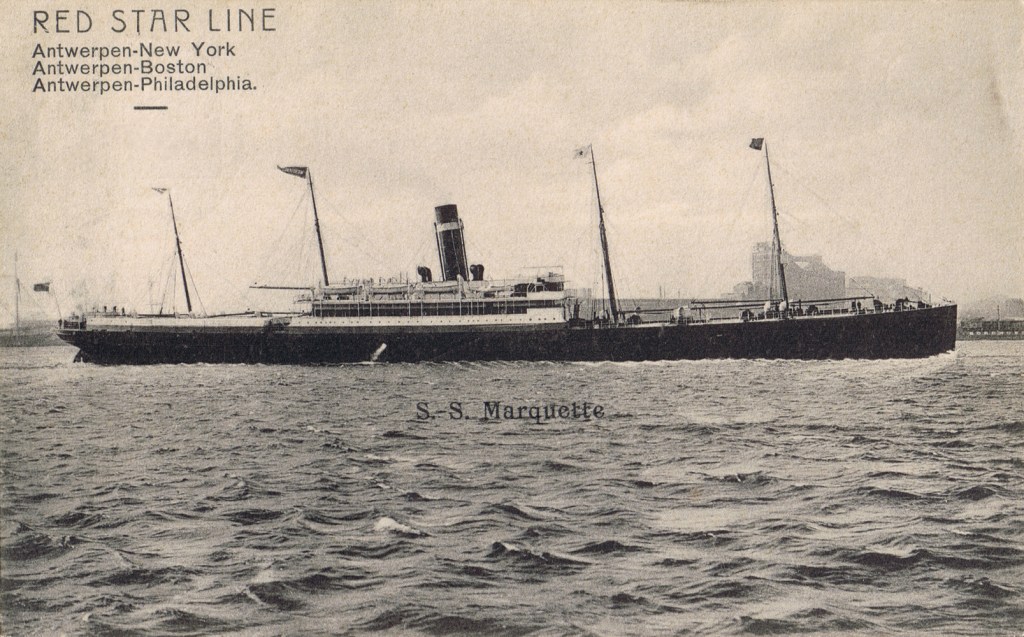

Image source: https://ww100.govt.nz/no-ordinary-transport-the-sinking-of-the-marquette
When it departed from Alexandria on 19 October, it carried medical personnel, British troops, over 500 mules, and ammunition. Although accompanied by a French destroyer during part of the journey, the escort departed the day before the attack.
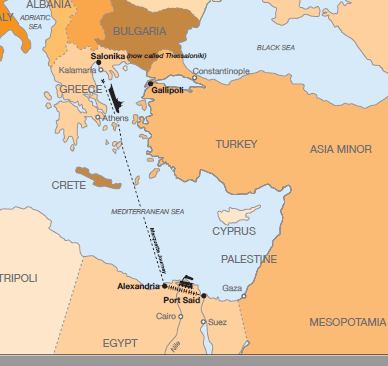
At approximately 9:15 a.m., witnesses reported sighting a torpedo shortly before it struck the starboard side of the ship. The impact caused the vessel to list sharply. Despite the suddenness of the event, many accounts describe those on board as remaining orderly.
Efforts to launch lifeboats were largely unsuccessful. Inexperienced personnel, the angle of the sinking ship, and mechanical difficulties led to lifeboats capsizing or being damaged. Several nurses and soldiers were killed during these attempts. It is believed that Margaret Rogers lost her life in this phase of the evacuation.
Ten New Zealand nurses and 22 men from the New Zealand Medical Corps and No. 1 Stationary Hospital died.
Survivors spent several hours in the water, exposed to cold conditions and exhaustion. Some clung to wreckage; others assisted colleagues unable to swim. Rescue vessels, including British and French destroyers, arrived later in the day. Six days later,on the 29th October, all surviving nurses and some medical officers returned to Alexandria on the hospital ship, the Grantully Castle.
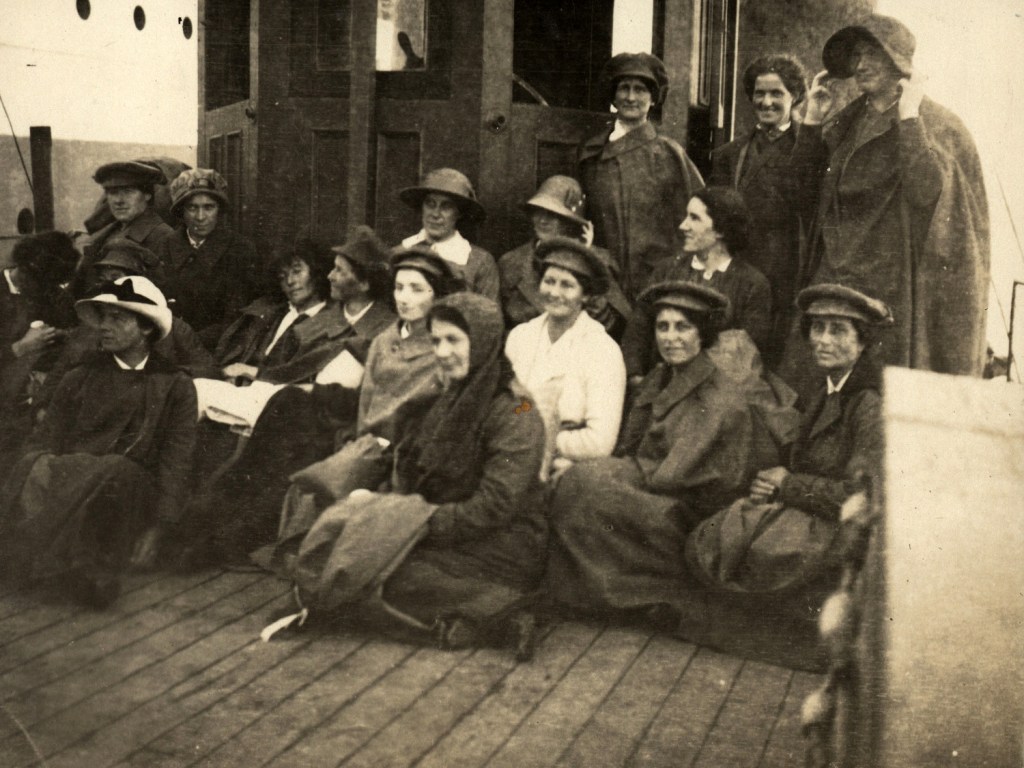

Image source: https://ww100.govt.nz/no-ordinary-transport-the-sinking-of-the-marquette
Aftermath
The sinking of the Marquette led to outrage about the decision to transport medical personnel on a vessel carrying ammunition and troops rather than on a hospital ship. Marked with a red cross, hospital ships could sail with a much greater degree of safety with the protection of the Geneva Convention. The troopship was, for German submarines, a valid target.
One can only imagine the emotions of the survivors as they undertook the journey to Salonika again later in the year in order to establish a tented hospital at Lembet Camp. The hospital was in operation until March 1916, when it left for France.

Image source: https://nzhistory.govt.nz/media/photo/1st-new-zealand-stationary-hospital
In Memory
Margaret Rogers is buried at the Mikra British Cemetery at Kalamaria where there is a memorial to the loss of the Marquette.

Margaret is also listed on the war memorial at Akaroa where her father lived.

Image source: https://nzhistory.govt.nz/memorial/akaroa-war-memorial
Margaret and the other nine nurses lost in the Marquette sinking are remembered at the Nurses’ Memorial Chapel at Christchurch Hospital and at the Marquette Nurses’ Memorial at Waimate.
The events of 23 October 1915 are also dramatised in the Australian TV series, ANZAC Girls, which until December 31st, 2025 is freely available to view here.

Image Source: Episode 3, https://player.stv.tv/summary/all3-anzac
Footnote
Wreckage of the Marquette was found in May 2009 by a Greek dive team. It rests in 87 metres of water of the Thermaikos Gulf in the North Aegean Sea. A protection order for the wreck has been sought by The British Embassy in Greece.
Reference Links
- https://www.armymuseum.co.nz/2023-today-in-history-marquette-sinking/
- https://ww100.govt.nz/no-ordinary-transport-the-sinking-of-the-marquette
- https://nzhistory.govt.nz/media/video/marquette-great-war-story
- https://ww100.govt.nz/no-ordinary-transport-the-sinking-of-the-marquette
- https://www.cnmc.org.nz/the-marquette/
- https://www.rnz.co.nz/news/national/287792/%27all-of-a-sudden-there-was-this-bang%27
- https://www.cnmc.org.nz/resources/museum/prentice-papers/
Screening in London: ‘By Far Kaymakchalan’ – A Documentary by Bojan Pajic
Those in London, or able to visit, on Saturday 18 October are warmly invited to attend the screening of By Far Kaymakchalan, a newly completed documentary by Australian writer and historian Bojan Pajic. The one-hour film will be shown from 3:00 to 5:00 pm in Room KIN 204, King’s College London, King’s Building, Strand Campus, WC2R 2LS.
Bojan Pajic is the author of two books examining the experiences of Australians and New Zealanders who served with Serbian forces during the First World War. By Far Kaymakchalan builds on his previous work and combines archival material, personal testimonies, and historical analysis to illuminate the shared history of these Allied nations. The event, hosted by Dr Stephen Morgan, Lecturer in Film Studies at King’s College London, will be followed by a discussion with Bojan Pajić.
Filmed in Australia, Serbia, Greece, and North Macedonia over a period of eighteen months, By Far Kaymakchalan is based on Pajić’s research that has revealed that more than 1,500 Australian and New Zealand volunteer doctors, nurses, ambulance drivers, soldiers, sailors, and aircrew served alongside Serbian forces during the war.
Full details of the event are available via this link.
NB For security reasons, King’s College London requires a list of attendees to be submitted 24 hours in advance. If you are thinking of attending, please don’t forget to register beforehand.
This screening offers a rare opportunity to engage with a significant and often overlooked chapter of First World War history, and to hear directly from the researcher and filmmaker who has dedicated much of his work to bringing these stories to light.
I’m very grateful to Jon Lewis, author of the excellent The Forgotten Front; the Macedonian Campaign 1915 – 1918, for bringing this to the attention of the Society – thanks Jon!
See also: https://salonikacampaignsociety.org.uk/2020/09/26/australians-and-new-zealanders/
Another Salonika connection … ?
I don’t think I have ever written here on Gallipoli, except in passing about those troops who went on to Salonika. I mean no disrespect to those of all nations who fought and died in the Gallipoli campaign but, with no family connections to the campaign, as with so many other areas of the First World War, I have had no more than a passing interest. I will admit, too, to a little irritation that with the landings in Gallipoli coming so hard on the heels of the start of the Second Battle of Ypres, this latter battle is so often overlooked (see Tuesday’s post). However, I have now had to revise my opinion.
Continue reading “Another Salonika connection … ?”Now online – Nick Ilic’s lecture on Sir Thomas Lipton and Serbia during WW1
On 9th February Colonel (Retd) Nick Ilic gave an online talk about Sir Thomas Lipton (1848–1931), the Scottish businessman and philanthropist best known for founding the Lipton tea company. I wrote an introduction to the talk here.
I’ve just spotted, rather belatedly, that Nic’s talk is now available on YouTube.
Nick Ilic lecture on Sir Thomas Lipton and Serbia during WW1
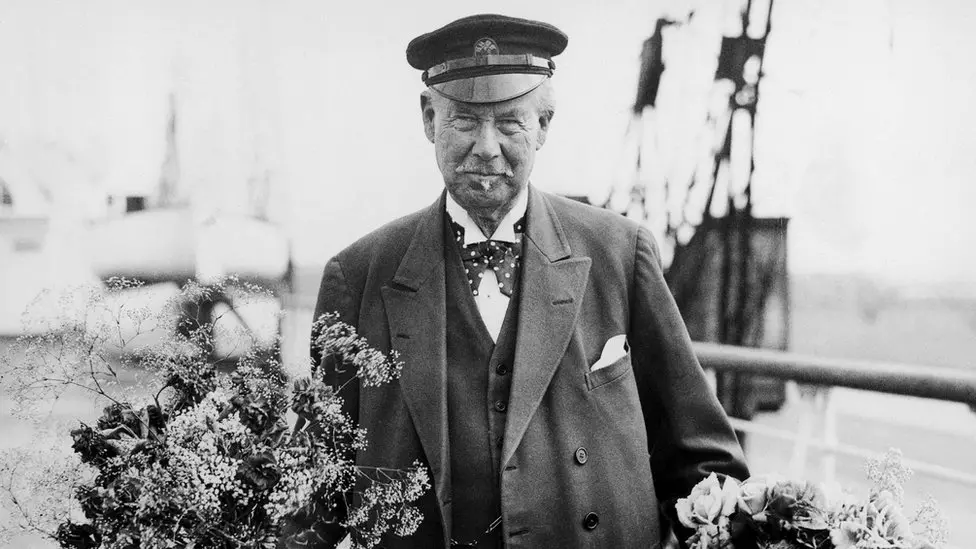

Sir Thomas Lipton (1848–1931) was a Scottish businessman and philanthropist best known for founding the Lipton tea company, which became one of the largest tea brands in the world. He was also a noted sportsman, famously competing in the America’s Cup yacht races several times, and made significant contributions to charity and education throughout his life.
During World War I, Lipton visited Serbia to offer humanitarian aid, moved by the suffering caused by the conflict. Recognizing the dire need for medical support, he donated substantial funds and medical supplies to assist Serbian soldiers and civilians, especially during the devastating 1915 retreat. His efforts helped establish field hospitals and provided relief to those affected by both the war and the widespread disease in the region.
This remarkable, and to me at least, largely forgotten story will be told with much more skill and knowledge by Colonel (Retd) Nick Ilic in a free online talk this week. As Nick explains, “It is a fascinating story and I’ve assembled a large number of photographs to try and bring it to life.”
The talk is on 11 February at 7pm and should last about an hour. You can join via this link:
- Join Zoom Meeting https://us06web.zoom.us/
- Meeting ID: 837 1461 6886 Passcode: 327477

